Patient Resources
Infertility Facts
Delve into critical insights with our detailed page on infertility, offering a comprehensive overview of key facts and statistics that shed light on this complex, often misunderstood medical issue.

Female Infertility: Why Can’t I Get Pregnant?
Understand the factors influencing female fertility and uncover a spectrum of treatment options for those seeking to expand their family.
Symptoms of Female Infertility
Female infertility is defined as trying to conceive for at least a year (six months if you’re over 35) with no success. Below are common signs and symptoms that may mean you need help getting pregnant:
Irregular, painful, or lack of a period
Hormonal fluctuations
Increased body weight
Advanced age
Pain during sex or lack of sex drive
About 11% of women of reproductive age in the U.S. have experienced fertility problems.
Women are only half as fertile once they reach their 30s. After 35, a woman’s chance of conception declines significantly.
Female infertility factors contribute to approximately 50% of all infertility cases.
Causes Of Female Infertility
We’ll take a closer look at common issues like Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS), reduced egg quality, tubal blockage, and primary ovarian insufficiency. Our goal is to provide insights and solutions to help you understand and address these fertility challenges.
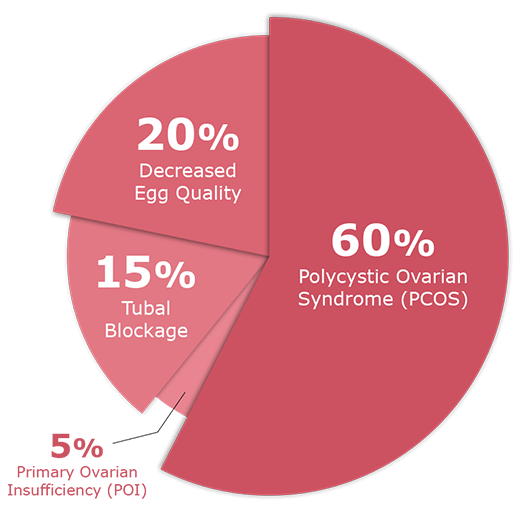
Treatments for Female Infertility
Female treatment options will depend on the cause of the initial problem, the age of the woman, history of any previous pregnancies, the male factor, and how long infertility issues have been known. Below are some common treatment options when it comes to female infertility:
Hormone Medications
Oral medication that allows the female body to produce more of the hormones that cause the eggs to mature in their ovaries.
Gonadotropins or Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
- Hormone injections that stimulate the eggs growth within the ovaries, leading to successful ovulation.
- Injections occur during the early stages of menstruation, for 7 to 12 days. As the woman is being treated, a doctor will monitor the growth of the eggs through an ultrasound.
Letrozole
- An oral pill to help decrease the amount of estrogen a woman is producing, which then will stimulate her ovaries for the release of eggs.
- Oral medication is taken during the first stages of menstruation, for about 3 days.
Surgical Treatments
May be necessary when it comes to the following infertility causes:
Disease of the fallopian tubes
- Surgery can repair or remove blockages
Ectopic pregnancy, which is when the pregnancy occurs outside of the uterus.
- Surgery of the fallopian tube is done in an effort to help fix these tubal pregnancies.
Patches of endometriosis
- Surgery is done to help remove these patches, doubling the chances of a pregnancy.
- Surgery can also be done in an effort to remove scarring, polyps, or uterine fibroids.
Health Conditions
In addition to medication and surgical treatments for female infertility, treatments to help specific health conditions called assisted reproductive technologies (ART) are available. The most common treatments in this category include:
“One of the most common questions that I’m frequently asked is what can I do in order to increase my chances of getting pregnant, and I would say that depends on your general state of health at this point in time.”
— Dr. Eva Littman

Male Infertility
Explore Causes and Solutions. Learn about the factors affecting male fertility and discover potential treatments.
Symptoms of Male Infertility
Aside from being unable to conceive a child, other signs and symptoms of male infertility include:
Issues with erection, ejaculation, or sexual function
Any pain discomfort, or swelling in the testicle area
Prior history of testicular, prostate or sexual problems
Previous groin, testicle, penis or scrotum surgery
9.4% of males in the U.S. are infertile.
For males between 41-45, fertility declines by up to 7% with every additional year of a man’s age.
Causes Of Male Infertility
Here are factors that contribute to fertility challenges in men, including medical, environmental, and health and lifestyle causes. Our aim is to help you understand and find solutions for these issues.
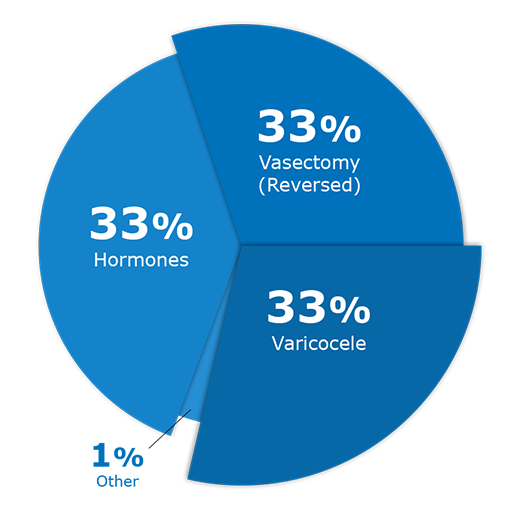
Treatments for Male Infertility
Treatment options for male infertility vary depending on the underlying causes, the man’s age, any history of previous pregnancies, the female partner’s health, and the duration of infertility issues. Here, we explore common approaches to address male infertility and restore reproductive health:
Hormone Medications and Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
- A medication that prompts the pituitary gland to make the hormones that direct the testicles to produce more testosterone and more sperm.
- HCG stimulates the testes to produce testosterone and sperm. And sometimes fertility drugs are used with ART treatment.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery for a varicocele
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes include:
Diet
- Eat a healthy and well-balanced diet full of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- “I always encourage my male patients to eat a lot of broccoli, spinach, and asparagus which are all very high in folic acid. And then, to eat blueberries, raspberries, and pomegranates, all of these fruits are very high in antioxidants.” (Dr. Littman, video transcript)
Alcohol and drug use
- Avoid cigarettes and any drugs that may affect sperm count or sexual function
Exercise
- Exercise regularly to reduce risk of obesity, which can be associated with infertility